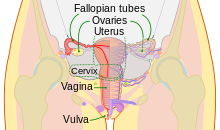
Female Reproduction System
At certain intervals, the ovaries release an ovum, which passes through the Fallopian tube into the uterus. If, in this transit, it meets with sperm, a single sperm can enter and merge with the egg, fertilizing it.
Fertilization usually occurs in the Fallopian tubes and marks the beginning of embryogenesis. The zygote will then divideover enough generations of cells to form a blastocyst, which implants itself in the wall of the uterus. This begins the period of gestationand the embryo will continue to develop until full-term. When the fetus has developed enough to survive outside the uterus, the cervix dilates and contractions of the uterus propel the newborn through the birth canal (the vagina).
organs
The female internal reproductive organs are the vagina, uterus, Fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular (made up of fibrous and muscular tissue) canal leading from the outside of the body to the cervix of the uterus or womb. It is also referred to as the birth canal in the context of pregnancy. The vagina accommodates the male penisduring sexual intercourse. Semen containing spermatozoa is ejaculated from the male at orgasm, into the vagina potentially enabling fertilization of the egg cell (ovum) to take place.
Cervix
The cervix is the neck of the uterus, the lower, narrow portion where it joins with the upper part of the vagina. It is cylindrical or conical in shape and protrudes through the upper anterior vaginal wall. Approximately half its length is visible, the remainder lies above the vagina beyond view. The vagina has a thick layer outside and it is the opening where the fetus emerges during delivery.
Uterus
The uterus or womb is the major female reproductive organs. The uterus provides mechanical protection, nutritional support, and waste removal for the developing embryo (weeks 1 to 8) and fetus (from week 9 until the delivery). In addition, contractions in the muscular wall of the uterus are important in pushing out the fetus at the time of birth.
The uterus contains three suspensory ligaments that help stabilize the position of the uterus and limits its range of movement. The uterosacral ligaments keep the body from moving inferiorly and anteriorly. The round ligaments restrict posterior movement of the uterus. The cardinal ligaments also prevent the inferior movement of the uterus.
The uterus is a pear-shaped muscular organ. Its major function is to accept a fertilized ovum which becomes implanted into the endometrium, and derives nourishment from blood vessels which develop exclusively for this purpose. The fertilized ovum becomes an embryo, develops into a fetus and gestates until childbirth. If the egg does not embed in the wall of the uterus, a female begins menstruation.
Fallopian tube
The Fallopian tubes are two tubes leading from the ovaries into the uterus. On maturity of an ovum, the follicle and the ovary's wall rupture, allowing the ovum to escape and enter the Fallopian tube. There it travels toward the uterus, pushed along by movements of cilia on the inner lining of the tubes. This trip takes hours or days. If the ovum is fertilized while in the Fallopian tube, then it normally implants in the endometriumwhen it reaches the uterus, which signals the beginning of pregnancy.
Ovaries
The ovaries are small, paired organs located near the lateral walls of the pelvic cavity. These organs are responsible for the production of the egg cells (ova) and the secretion of hormones. The process by which the egg cell (ovum) is released is called ovulation. The speed of ovulation is periodicand impacts directly to the length of a menstrual cycle.
After ovulation, the egg cell is captured by the Fallopian tube, after traveling down the Fallopian tube to the uterus, occasionally being fertilized on its way by an incoming sperm. During fertilization the egg cell plays a role; it releases certain molecules that are essential to guiding the sperm and allows the surface of the egg to attach to the sperm's surface. The egg can then absorb the sperm and fertilization can then begin.[citation needed]The Fallopian tubes are lined with small hairs (cilia) to help the egg cell travel.
Physiology
The reproductive tract (or genital tract) is the lumen that starts as a single pathway through the vagina, splitting up into two lumens in the uterus, both of which continue through the Fallopian tubes, and ending at the distance ostiathat open into the abdominal cavity.
In the absence of fertilization, the ovum will eventually traverse the entire reproductive tract from the fallopian tube until exiting the vagina through menstruation.
The reproductive tract can be used for various transluminal procedures such as fertiloscopy, intrauterine insemination, and transluminal sterilization.
development
Chromosome characteristics determine the genetic sex of a fetus at conception . This is specifically based on the 23rd pair of chromosomes that is inherited. Since the mother's egg contains an X chromosome and the father's sperm contains either an X or Y chromosome, it is the male who determines the fetus's sex. If the fetus inherits the X chromosome from the father, the fetus will be a female. In this case, testosterone is not made and the Wolffian duct will degrade thus, the Müllerian duct will develop into female sex organs. The clitoris is the remnants of the Wolffian duct. On the other hand, if the fetus inherits the Y chromosome from the father, the fetus will be a male. The presence of testosterone will stimulate the Wolffian duct which will bring about the development of the male sex organs and the Müllerian duct will degrade.
Reproductive rights
The International Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics was founded in 1954 to promote the well-being of women particularly in raising the standards of gynaecological practice and care. As of 2010 there were 124 countries involved.
Reproductive rights are legal rights related to reproduction and reproductive health. Women have the right to control matters involving their sexuality including their sexual and reproductive health. Violation of these rights include forced pregnancy, forced sterilization, forced abortion and genital mutilation. Female genital mutilation is the complete or partial removal of a female's external genitals .



Comments
Post a Comment